In paid search advertising, audiences are key to success. By effectively segmenting your target markets, you can improve bidding and targeting, boosting overall campaign performance.
Introduction to Google Ads Audiences
Reaching the right people is essential for effective advertising. Your ability to connect with the right audience determines your market success. Google Audience empowers you to achieve this goal.
Recently, Google has made some improvements with regards to Audiences:
- Audience data, including demographics, segments, and exclusions, is now organized in a single location.
- The term “audience types” has been replaced with “audience segments” for greater clarity.
- “Remarketing” is now being referred to as “your data” to reflect its role in targeting better.
Types of Audience Targeting
Audience targeting in Google Ads search campaigns allows you to show your ads to people most likely to be interested in your products or services. This can help you to ensure that the right people see your ads.
Here are the available audience types in Google ads:
1. Detailed Demographic: With this audience targeting, we can reach potential customers within a specific age range, household income, gender, and parental status. This way, advertisers filter their audience targeting further.
2. Affinity Audience: With Affinity audiences, Google Ads allows you to reach people based on their interests and habits. These audiences are based on Google’s understanding of people’s online behaviour.
3. In-Market Audience:
This audience type helps find potential buyers who are out there in the market and searching to buy products or services you offer. An in-market audience is quite helpful for advertisers who are focused on getting conversions from a potential buyer.
For example, suppose a person is reading reviews about smartphones and watching videos to know the features. In that case, Google might consider him a potential smartphone buyer and put him in a relevant In-Market audience.
4. Your Data: Earlier, your data was known as the “Remarketing audience“. This helps to re-engage people who have previously interacted with your brand or services on mobile or desktop.
5. Combined Segments: A combined segment in Google Ads is a way to target your ads to people with more than one audience segment. This allows you to create more specific and effective targeting strategies by intersecting different audience attributes, such as demographics, interests, and behaviours.
6. Custom Segments: In Google Ads, Custom Segments serve as a targeting functionality that empowers advertisers to create extremely refined audience segments. This can be set up in your Discovery, Gmail and video campaigns by specifying criteria like keywords, URLs, and apps.
Leveraging Google Ads Audience Targeting Effectively
Google Ads audience targeting allows you to reach specific groups of users, increasing the likelihood of connecting with potential customers who are genuinely interested in your products or services. Here are a few ideas to leverage this powerful tool effectively:
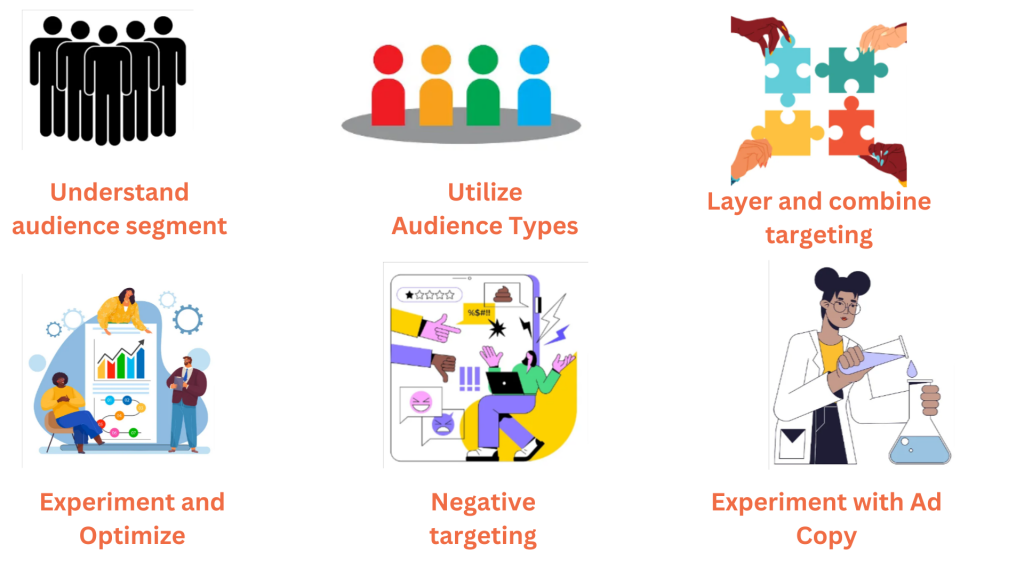
1. Understand your audience segment: Before diving into targeting options, clearly define who your ideal customer is. Use Google Analytics, customer surveys, and other data sources to gather insights into your audience’s preferences and online behaviour. This will guide your targeting choices and ensure your ads reach the right people.
2. Utilize Google Ads Audience Types: Take advantage of the various audience types offered by Google Ads. When ads are tailored to specific audience segments, they become more relevant and engaging. This leads to higher click-through rates and improved conversion rates.
3. Layer and combine targeting: Don’t limit yourself to single targeting layers. Instead, combine different options for a more refined audience selection. For instance, target users aged 25-34 (demographics) interested in travel (Affinity) have visited the website but haven’t booked a trip (Your data or remarketing list).
One can also combine targeting options using “and” for a narrower audience or “or” for a broader audience. For example, target users “and” interested in travel “and” have visited your website “or” have purchased travel insurance from a competitor.
4. Experiment and Optimize: Experiment with different targeting combinations and monitor ad performance metrics like click-through rate, conversion rate and ROAS. Analyze data to identify what works best and refine your targeting accordingly.
5. Negative targeting: Exclude irrelevant audiences to prevent wasted ad spend and ensure your ads reach only the most qualified potential customers.
6. Experiment with Ad Copy and Creatives: Adapt your ad content and designs to connect with different audience groups. Experiment with various messages and visuals to find what resonates most with each target audience.
Remember that audience targeting is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring and optimization. By following these keys, you can leverage Google Ads audience targeting effectively, reach the right audience with your ads, and optimize your campaign performance for greater success.
Related Links





Stop the wasted ad spend. Get more conversions from the same ad budget.
Our customers save over $16 Million per year on Google and Amazon Ads.